- What is EB?
- About EB
- Types of EB
- Inheritance of EB
- Finding a Cure
- Want to know more?
- Acknowledgements
Junctional EB (JEB)
JEB is the least common form of EB, constituting about 10% and is inherited in a recessive manner. The responsible mutation is usually in the genes for laminin 5 (laminin 332), or collagen XVII or alpha-6-beta-4 integrin. The skin comes apart at a level between EBS and DEB but somewhat paradoxically, wounds in JEB may take the longest to heal.
- Herlitz JEB is the most severe subtype - blistering often gets worse after birth with diapering and bathing, the fingers/ toes and face are also often affected. Wounds tend to heal slowly as the laminin defects also affects the function of skin cells (keratinocytes) and pain is often significant. Babies may develop a hoarse cry due to continual blistering and scarring of the vocal cords. The prognosis is poor; those with severe generalized disease often die in infancy due to malnutrition and anaemia.
- Enamel defects often mean caries
 Stay in Touch
Stay in Touch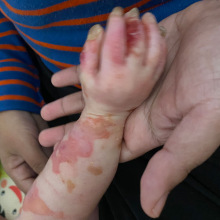 Wudy’s story
Wudy’s story(translated by Google Translate)
Married for seven years, long-awaited first-time mother when I thought I was happiest... read more
